Definition Of Buffer System In Biology
A buffer system has the property of resisting pH changes despite additions of acid or base. Learn the definition of a buffer system understand how it works and assess your knowledge with a quiz.
 What Is A Buffer And How Does It Work Westlab
What Is A Buffer And How Does It Work Westlab
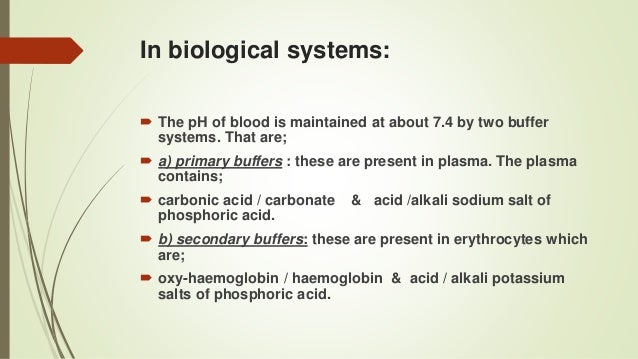
As a buffer it tends to maintain a relatively constant plasma pH and counteract any force that would alter it.

Definition of buffer system in biology. For example the bicarbonate buffering system is used to regulate the pH of blood. A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. In nature there are many systems that use buffering for pH regulation.
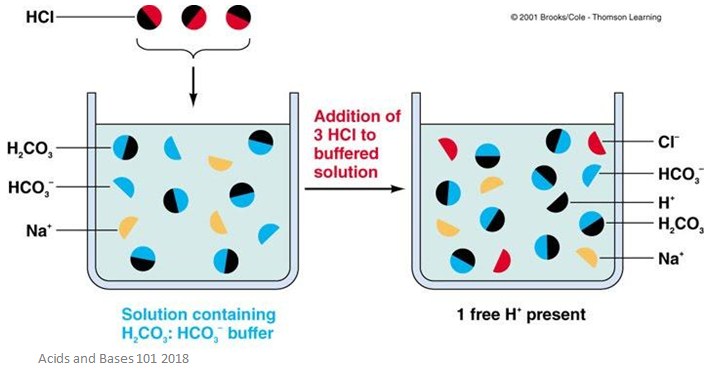
Buffer systems are made of either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt. If acid is added to this buffer the added H ions combine with bicarbonate ions to produce more carbonic acid using up some of the H ions the Na ions do not participate in this reaction. It keeps the pH within the proper range.
1 A chemical system that minimises the effectsin particular the pHof changes in the concentration of a substance. You might not require more times to spend to go to the ebook commencement as competently as search for them. A biological buffer is an organic substance that has a neutralizing effect on hydrogen ions.
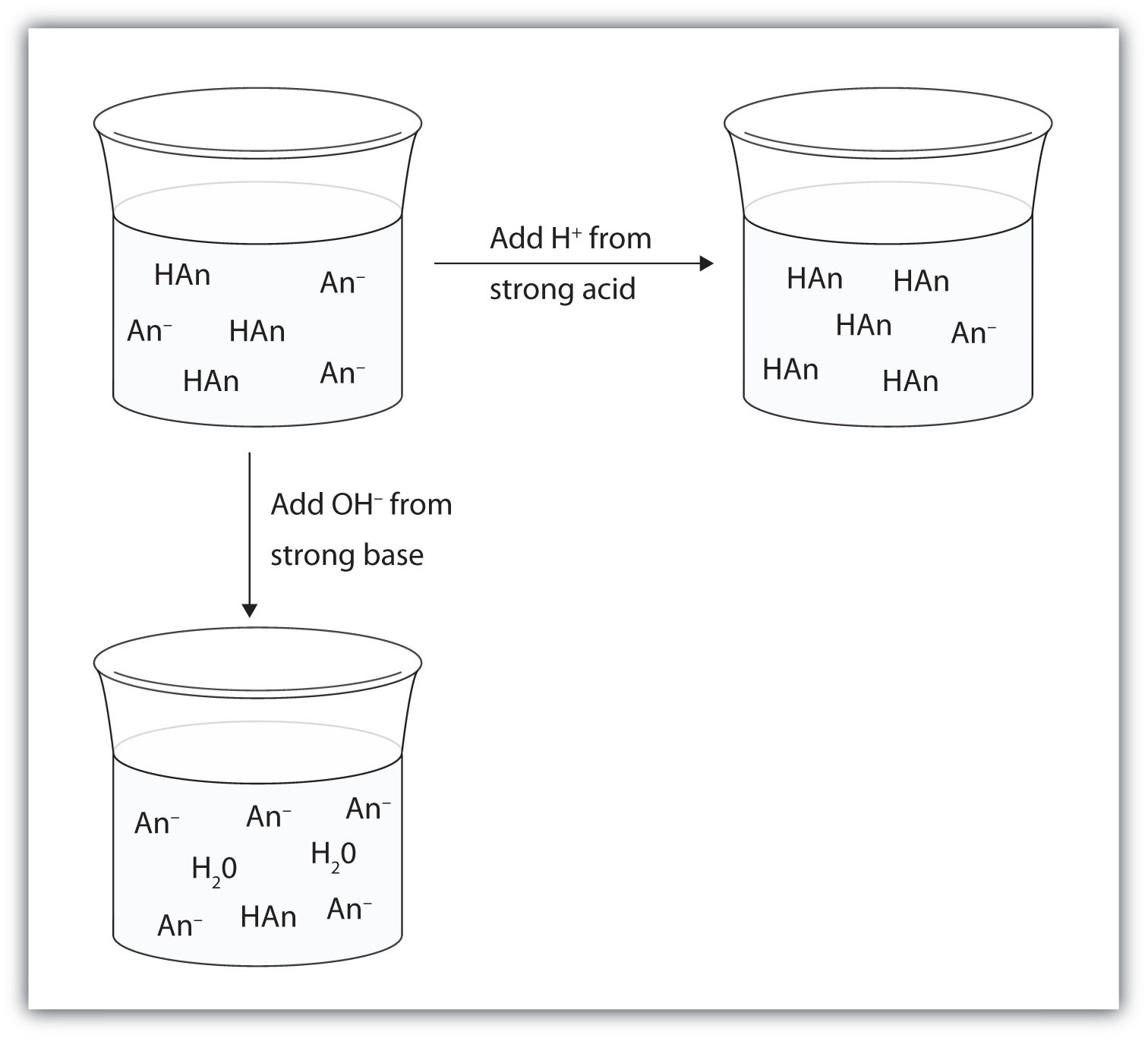
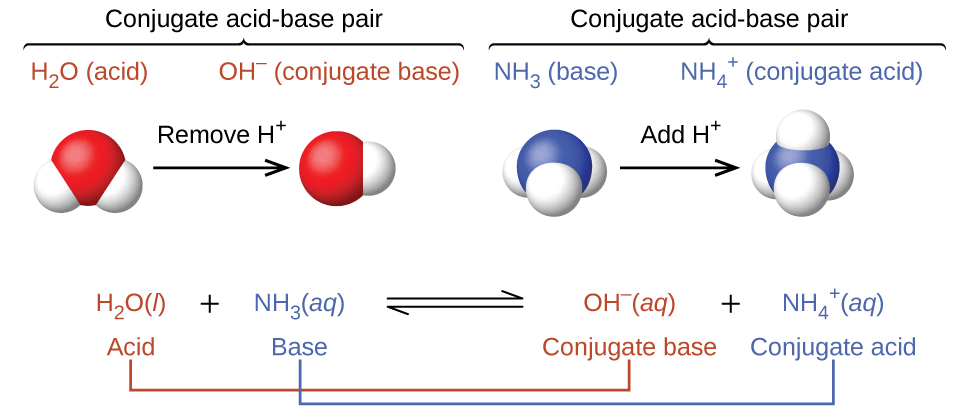
A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. High School Biology. When an acid or alkali has added the pH of the solution changes in the absence of buffers.
2 A molecule that serves to prevent large changes in pH by either combining with H or by releasing H into solution. Buffer Systems also buffer solutions or buffer mixtures systems that maintain a certain concentration of H ionsthat is a certain acidity of the medium. In many ways our lives are dependent on functioning buffer systems.
Buffers are the mixture of weak acids and their salts of strong bases or the mixture of weak bases and their salts of strong acids. A buffer system consists of a weak acid the proton donor and its conjugate base the proton acceptor. A buffer is a chemical system designed to prevent dramatic alterations in fluid pH by binding up any changes in hydrogen ion concentrations due to excess acid or base production.
Buffers are the key. Buffers readily absorb excess H or OH keeping the pH of the body carefully maintained in the aforementioned narrow range. A buffer system is a solution that resists change in pH when acids or bases are added to it.
Access Free Buffer Solution Definition Biology Buffer Solution Definition Biologypdfatimesi font size 12 format This is likewise one of the factors by obtaining the soft documents of this buffer solution definition biology by online. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffer hydrogen ion buffer or buffer solution.
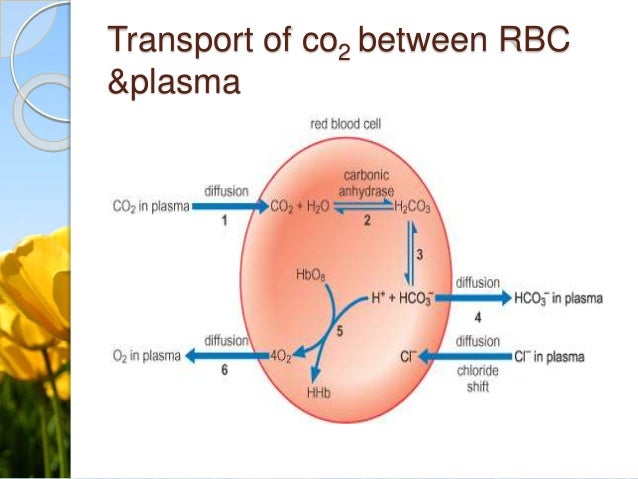
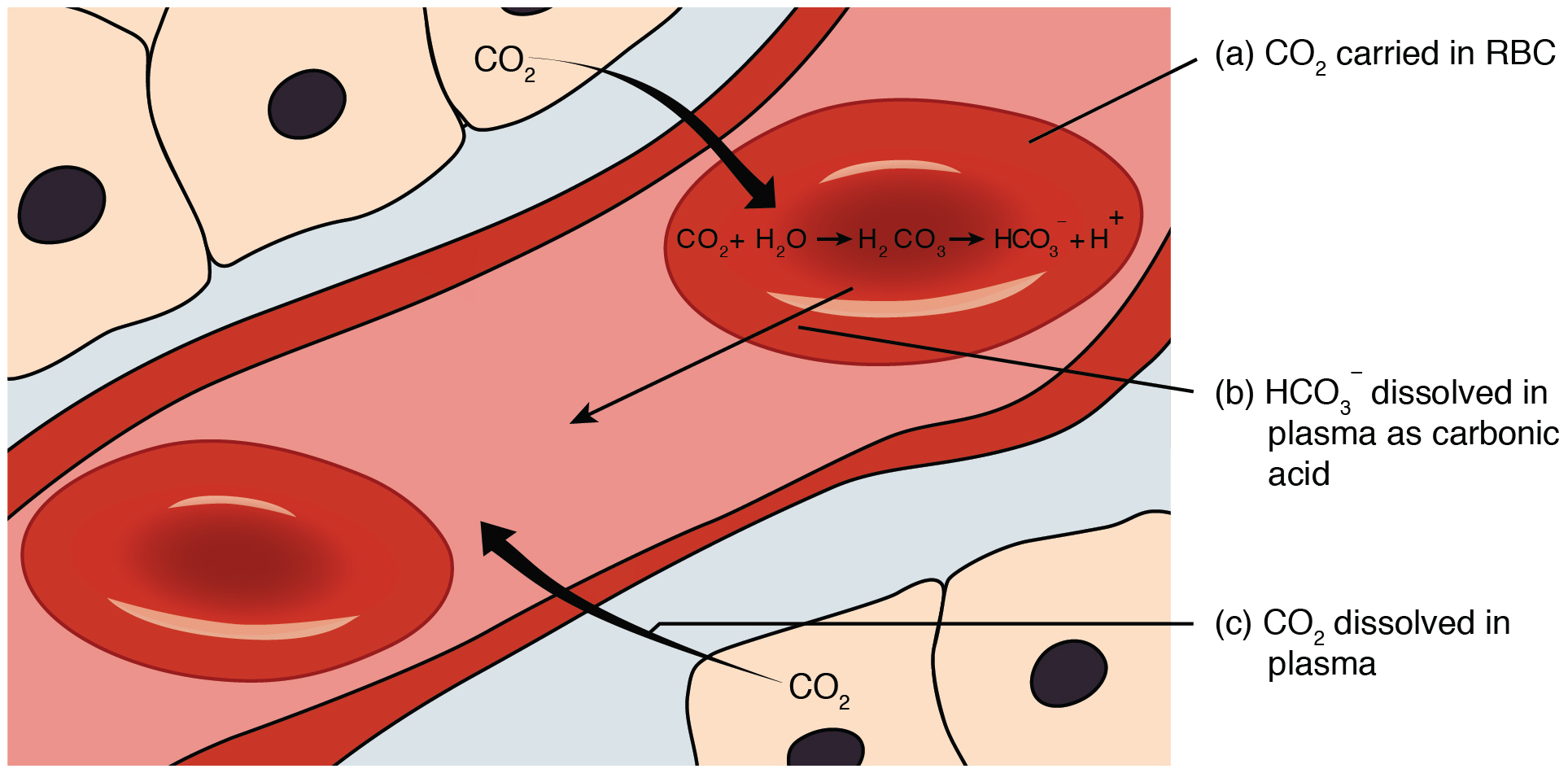
This buffer system involves carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 and bicarbonate HCO 3 anion. Most buffers consist of a weak acid and a weak base. Biceps The bicarbonate buffering system is an important buffer system in the acid-base homeostasis of living things including humans.
Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. The acidity of buffer solutions changes little when they are diluted or when certain amounts of acids or bases are added. Buffers typically consist of an acid-base pair with the acid and base differing by the presence or absence of a proton a conjugate acid-base pair.
Buffers help to maintain a normal pH of the biological systems. A buffer is an aqueous solution used to keep the pH of a solution nearly constant. For instance one of the buffers that maintain the pH of human blood involves carbonic acid H _2 2.
Buffers are the mixtures of weak acids and their salts of strong bases or strong acids and their salts of weak bases. Glossary - word Glossary - def Textbooks Protocols Images Tools Forum PubMed Links Press Releases. A buffer is a mixture of an acid that does not ionize completely in water and its corresponding base-for example carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 and sodium bicarbonate NaHCO 3.
Carbon dioxide is part of a prominent buffer system in the human body. In this way a biological buffer helps maintain the body at the correct pH so that biochemical processes continue to run optimally. Cells and organisms maintain a specific and constant cytosolic pH keeping biomolecules in their optimal ionic state usually near pH 7.
Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes. Buffer Definition - Chemistry and Biology DEFINITION A buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid its salt or a weak base its salt that resist a change in pH on the addition of either acid or base. Meaning of Buffer System.
 Acid Base Buffers Facts Summary Definition Chemistry Revision
Acid Base Buffers Facts Summary Definition Chemistry Revision
 Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
 10 5 Buffers The Basics Of General Organic And Biological Chemistry
10 5 Buffers The Basics Of General Organic And Biological Chemistry
 Buffers Definition Overview Expii
Buffers Definition Overview Expii
 Buffer Solutions Biochemistry The Biology Notes
Buffer Solutions Biochemistry The Biology Notes
 Biological Buffer Systems Youtube
Biological Buffer Systems Youtube
 Bicarbonate Buffer System Wikipedia
Bicarbonate Buffer System Wikipedia
 Buffer Buffering Capacity Properties Of Good Buffer And Role Of Buffer In Vitro And In Vivo Online Biology Notes
Buffer Buffering Capacity Properties Of Good Buffer And Role Of Buffer In Vitro And In Vivo Online Biology Notes
 Introduction To Buffers Water Acids And Bases Biology Khan Academy Youtube
Introduction To Buffers Water Acids And Bases Biology Khan Academy Youtube
 Lec 9 Level 4 De Biological Buffer
Lec 9 Level 4 De Biological Buffer
 Buffer Solutions Definition Types Preparation Examples And Videos
Buffer Solutions Definition Types Preparation Examples And Videos
 What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio
What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio
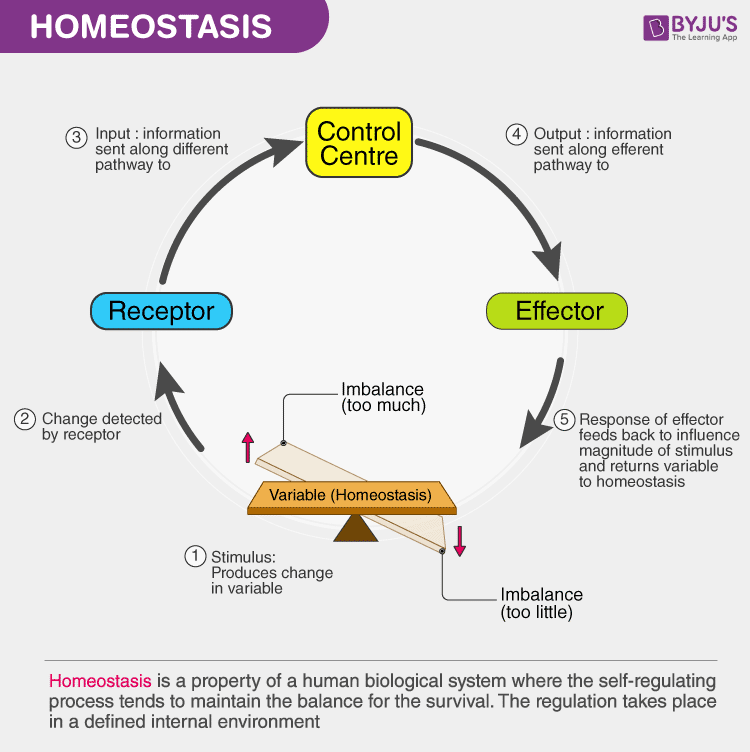 What Is Homeostasis Meaning Definition And Examples
What Is Homeostasis Meaning Definition And Examples
 Acids Bases Ph And Buffer Solutions A Level Biology Notes
Acids Bases Ph And Buffer Solutions A Level Biology Notes